Introduction
- Physicians and health care systems across the country have embraced a blend of in-person and virtual care, creating hybrid workflows that can adapt to the evolving needs of patients and the system at large.
- As the U.S. confronts an aging and growing population and an intensifying physician shortage,1 the adaptability and flexibility telemedicine can provide could prove more critical than ever. Additionally, as health care costs continue to rise and more hospitals consolidate and private practices close,2 telemedicine could offer a scalable solution that maintains patient access and continuity of care. By enabling remote consultations and disease management, telemedicine can help bridge gaps in patient care, particularly for rural or underserved communities and patients living with chronic illnesses.
- This report examines the evolving role of telemedicine, including its most effective applications, contributions to patient access and outcomes, and impact on physician productivity. Study findings show that the majority of physicians surveyed believe telemedicine has contributed to better disease management, improved patient outcomes and satisfaction, and equivalent or superior adherence to treatment plans. Physicians also report telemedicine has led to reduced patient wait times and missed appointments, while offering an opportunity to better understand and address their patients’ social determinants of health.
- As physicians continue to integrate telemedicine into their practices, more than three-fourths (77%) of physician telemedicine users surveyed reported using it at least weekly and more than one-third reported using it daily. From managing medications and chronic illnesses to reviewing lab tests and treatment options, physicians are using telemedicine to improve communication with their patients and expand access to care.
- The benefits of telemedicine are also resonating with patients. Among patients surveyed who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year, 96% said it resulted in equivalent or superior overall medical care, and 78% reported it improved their access to health care services. The strong majority (82%) also believe telemedicine has helped them stay up to date with their care.
- Looking ahead, most physicians and patients surveyed want to maintain access to telemedicine services. With telemedicine, physicians and the broader health care system can provide high-quality, flexible options that meet the evolving needs of patients.
Physician Adoption of Telemedicine
Physician Insights
Telemedicine Insights from Doximity’s Physician Membership
To gain a deeper understanding of telemedicine’s current role in health care delivery, Doximity analyzed how its physician members, across all specialties and practice areas, utilized its telemedicine tools throughout 2023.
As a supplement to this usage data, in August 2024, Doximity conducted a survey of 1,171 of its physician telemedicine users across ten specialties: cardiology, dermatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, neurology, oncology, primary care, psychiatry, pulmonology, and rheumatology.
New this year, Doximity also surveyed 131 of its nurse practitioner telemedicine users, providing a more comprehensive view of telemedicine adoption across the broader health care landscape.
Adoption by Physician Age
Telemedicine Use Remains Strong Across All Age Groups
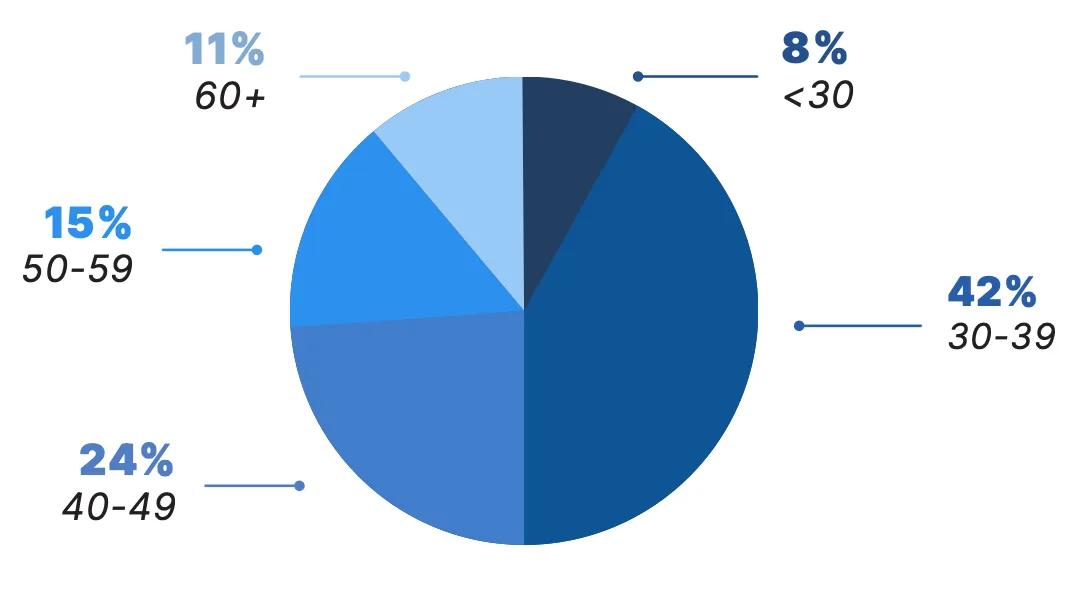
In 2023, telemedicine was utilized by physicians of all age groups. Physicians under the age of 50 accounted for nearly three-fourths (74%) of Doximity’s telemedicine users last year.
Telemedicine Physician Users by Age
Adoption by Physician Specialty
Telemedicine Adoption Remains Highest in Specialties that Manage Chronic Illness
Physicians in specialties that manage a significant number of patients with chronic illnesses continue to show some of the highest adoption rates of telemedicine. Patients with chronic illnesses often require ongoing medical attention, including frequent follow-up visits, symptoms monitoring, and medication management. By leveraging virtual visits, physicians can maintain regular touch points with their patients without requiring in-person visits for each interaction.
Top Specialties by Adoption Rate
| Specialty | |
|---|---|
| 1. Endocrinology | 11. Pulmonology |
| 2. Urology | 12. Internal Medicine |
| 3. Gastroenterology | 13. Allergy & Immunology |
| 4. Rheumatology | 14. Neurosurgery |
| 5. Neurology | 15. Family Medicine |
| 6. Otolaryngology (ENT) | 16. Pediatrics |
| 7. Nephrology | 17. Orthopaedic Surgery |
| 8. Dermatology | 18. Psychiatry |
| 9. Hematology/Oncology | 19. Vascular Surgery |
| 10. Cardiology | 20. Ophthalmology |
Frequency of Use
Many Physicians Incorporating Telemedicine into Daily, Weekly Practice
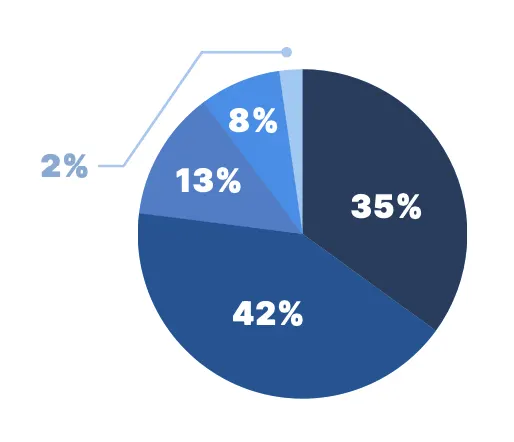
Over the past few years, telemedicine appears to have cemented its role in clinical practice. More than 77% of physician telemedicine users surveyed reported using it at least weekly, with more than one in three (35%) incorporating it into their daily clinical practice.*
Among the 10 physician specialties surveyed, the highest reported daily use of telemedicine was in psychiatry at 66%, followed by endocrinology at 48%. Additionally, nearly 31% of oncologists surveyed reported daily use.
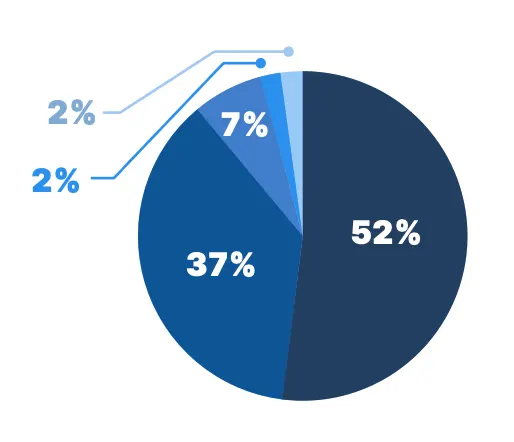
Notably, nurse practitioners reported some of the most frequent use of telemedicine. Among those surveyed, 89% said they use telemedicine at least weekly, with over half (52%) using it on a daily basis.

*The figures represent all forms of telemedicine used by the surveyed physicians and nurse practitioners.
How often do you use telemedicine in your practice?
MD/DO Telemedicine Users
NP Telemedicine Users
Flexibility of Use
Many Physicians Embracing Multiple Telemedicine Modalities, Hybrid Clinical Workflows
Physician adoption of telemedicine remains strong across various modalities and workflows. While video visits continue to be predominant, used by 88% of physicians surveyed, audio-only phone visits are also widely employed (67% of physicians).
Regardless of the telemedicine format, many physicians across specialties are embracing hybrid clinical workflows. Nearly half of physicians surveyed (46%) said they use telemedicine either at home or while on the go, and one-third said they work from home with telemedicine at least once per week.
Nurse practitioners also appear to be leaning into hybrid clinical workflows. Among those surveyed, 75% reported they use telemedicine either at home or while on the go, and over half (51%) reported they work from home with telemedicine at least once per week.
Telemedicine’s high usage both within and outside of the medical office reinforces the flexibility it can provide across the care continuum.
Where do you typically conduct your telemedicine visits?

Effects on Productivity, Work-Life Balance
Physicians Report Improvements to Workflow and Patient Care
Ongoing staffing shortages, administrative burden, and other daily frictions have made it increasingly difficult for physicians to best serve their patients. Still, physicians continue to find ways to increase their productivity — in part by integrating telemedicine services into their practices.3
Two-thirds of Doximity telemedicine users surveyed reported the technology has helped them better serve their patients, and nearly a third reported it has allowed them to serve more patients per day. A substantial percentage of physicians surveyed also reported telemedicine has allowed them to work more effectively from any location, made it easier to manage their schedule, and provided them with greater autonomy and work-life balance.
Productivity Benefits Reported by Physician Telemedicine Users
Range of Clinical Applications
Telemedicine Plays Multifaceted Role in Medicine
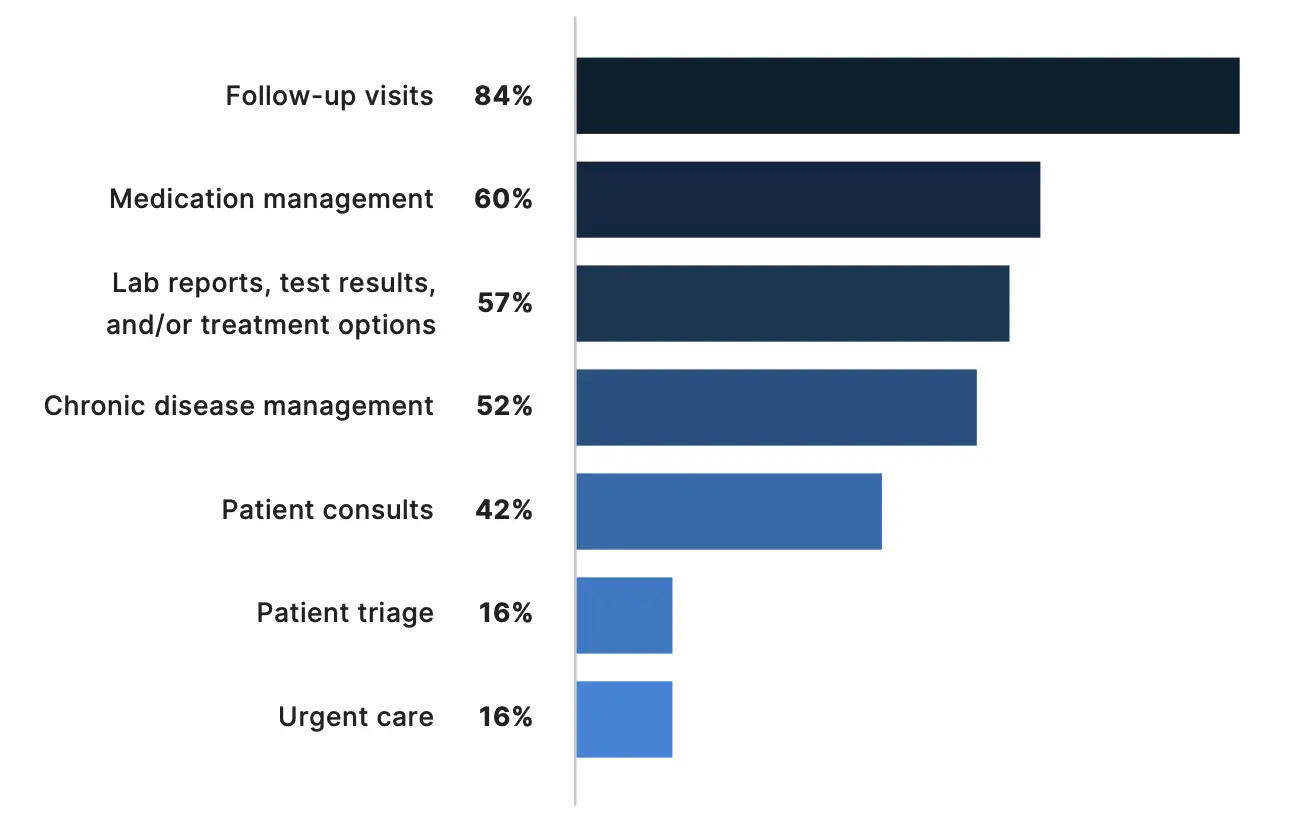
From routine visits to complex disease management, telemedicine can play an important role in a wide range of health care applications. More than 42% of physicians surveyed use telemedicine for patient consults, and 84% use it for follow-up visits. Beyond routine care, the majority of physicians surveyed rely on telemedicine to manage medications (60%) and chronic diseases (52%), and to discuss lab reports, test results, or treatment options with their patients (57%).
The integration of telemedicine in chronic disease management can be particularly beneficial for specialists. Nearly three-fourths of endocrinologists (73%) and 70% of rheumatologists surveyed said they use telemedicine for chronic disease management. Primary care physicians also reported using telemedicine frequently for medication management (74%) and to report results or treatment options (69%).

How Physicians Apply Telemedicine in Clinical Practice
Effects on Continuity of Care
Physicians Report Positive Impact on Continuity of Care, Disease Management
One of the most significant benefits of telemedicine could be its ability to enhance continuity of care and disease management, particularly for patients with chronic illnesses. Among physicians surveyed, 84% reported that telemedicine has proved useful in improving continuity of care for patients with chronic or complex conditions.
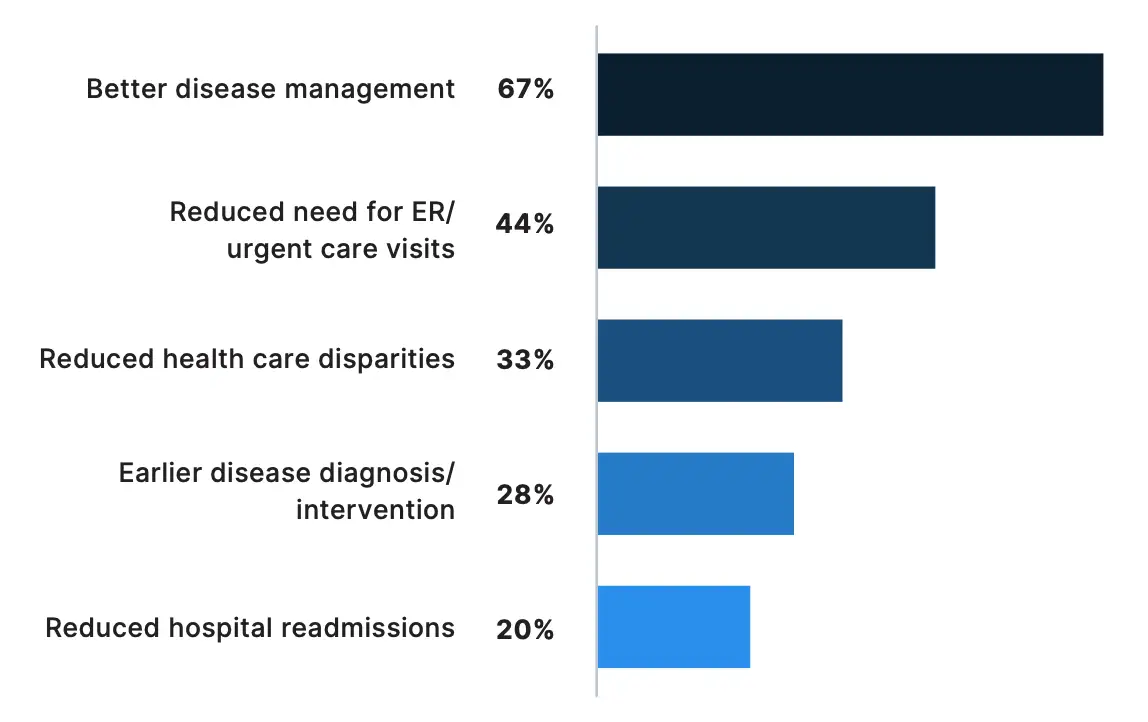
The majority of physicians surveyed (67%) also reported telemedicine has contributed to better disease management. This figure rises to 77% for oncologists, who manage patients with serious chronic illnesses. In fact, a quarter of oncology telemedicine users surveyed reported that telemedicine has contributed to earlier diagnosis and intervention.
Physicians have also observed the effects of telemedicine on preventive health care, including reducing the need for urgent care or emergency visits (44%) and hospital re-admissions (20%), and contributing to earlier disease diagnosis and intervention (28%). The reduction in urgent care or emergency visits due to telemedicine was particularly evident to primary care physicians (63% of those surveyed).
Which of the following patient care benefits have you observed as a result of telemedicine?
Effects on Patient Outcomes, Satisfaction
Physicians Report Improved Patient Outcomes, Satisfaction
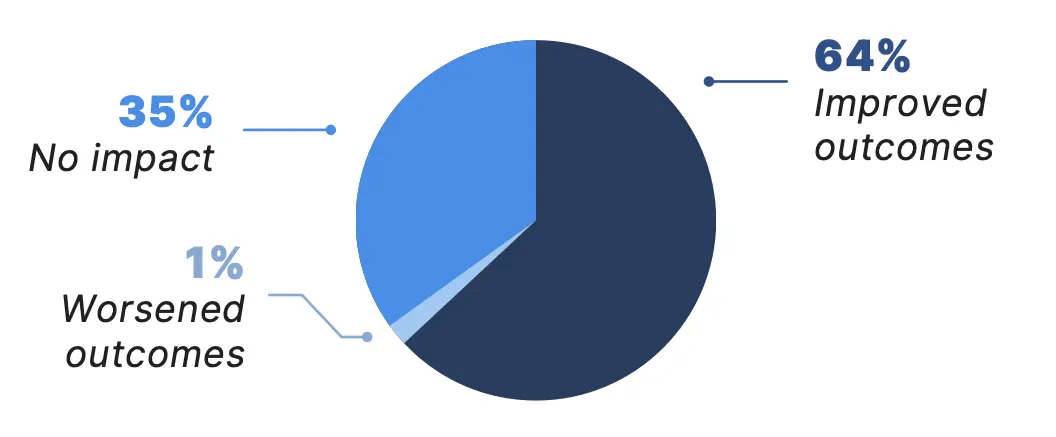
Collectively, the benefits of telemedicine appear to be having a meaningful impact on patient care. Among all physician telemedicine users surveyed, 64% reported telemedicine has improved patient outcomes in their practices. There was particularly broad agreement that telemedicine has improved patient outcomes among neurologists (72% agree), endocrinologists (70%), and rheumatologists (70%). Additionally, nearly 84% of physicians surveyed said telemedicine has increased patient satisfaction, with nearly 88% of oncologists confirming it has enhanced satisfaction among their patients.



How has telemedicine impacted patient outcomes in your practice?
How has telemedicine impacted patient satisfaction in your practice?*
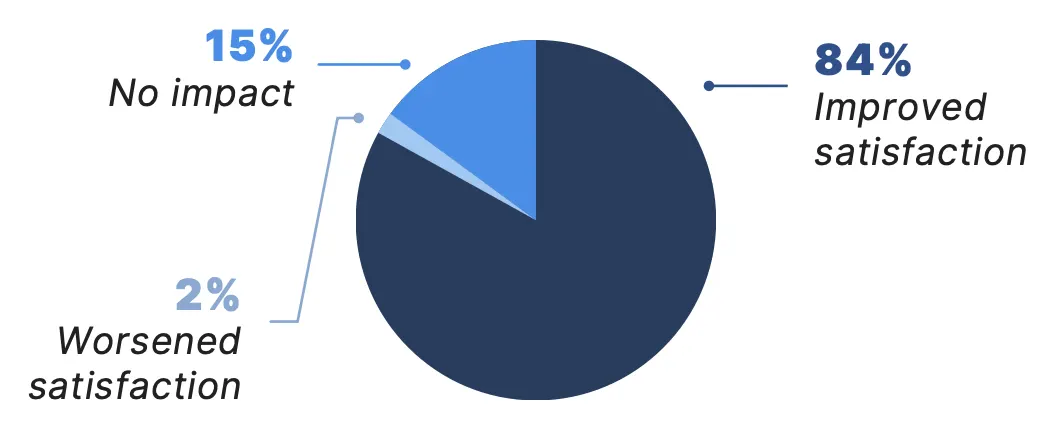
*Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Effects on Patient-Physician Relationship
Physicians Report Benefits to Patient Communication and Social Determinants of Health
Telemedicine appears to serve as a unique gateway into a patient’s home and daily life, offering valuable insight into the environmental and non-medical factors that can impact health outcomes. Among physicians surveyed, nearly 70% reported that telemedicine has helped them better understand and address their patients’ social determinants of health, with an additional 25% agreeing that they believe it can help.
Additionally, 98% of physicians surveyed reported that telemedicine has improved or sustained their level of communication with patients — further emphasizing the potential of telemedicine to strengthen physician-patient interactions.

Has telemedicine helped you better understand and address your patients’ social determinants of health?

How has telemedicine impacted your communication with your patients?*
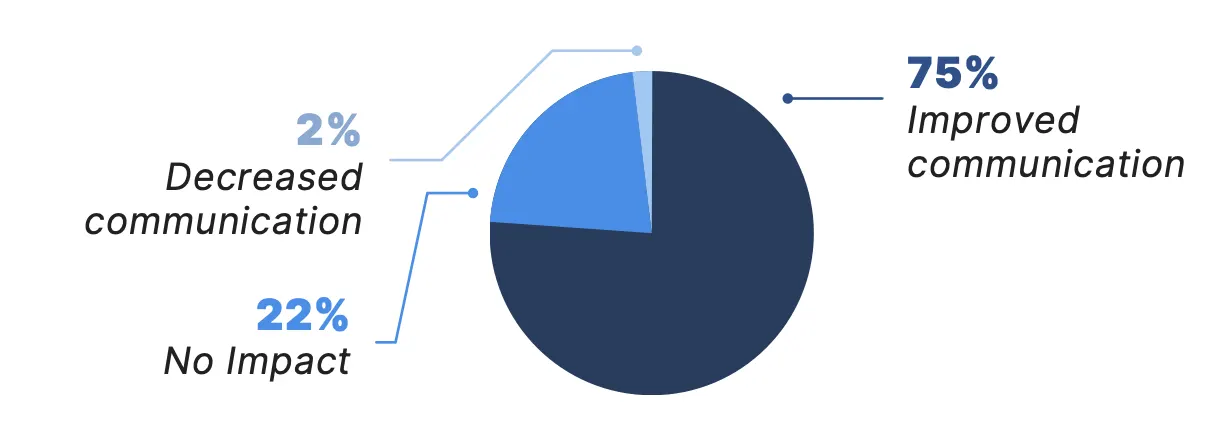
*Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Effects on Patient Access
Physicians Report Improved Access to Health Care Services
Telemedicine can help bring crucial services to people who have had limited or inequitable access in the past. More than 89% of physicians surveyed agreed that telemedicine has increased patient access to health care, particularly among populations that may previously have had difficulty accessing care — a slight increase from 88% last year.
Furthermore, 92% of physicians reported that telemedicine has enabled them to provide care to patients who face obstacles visiting their office in-person, up from 87% the prior year.
Has telemedicine increased patient access to health care?*
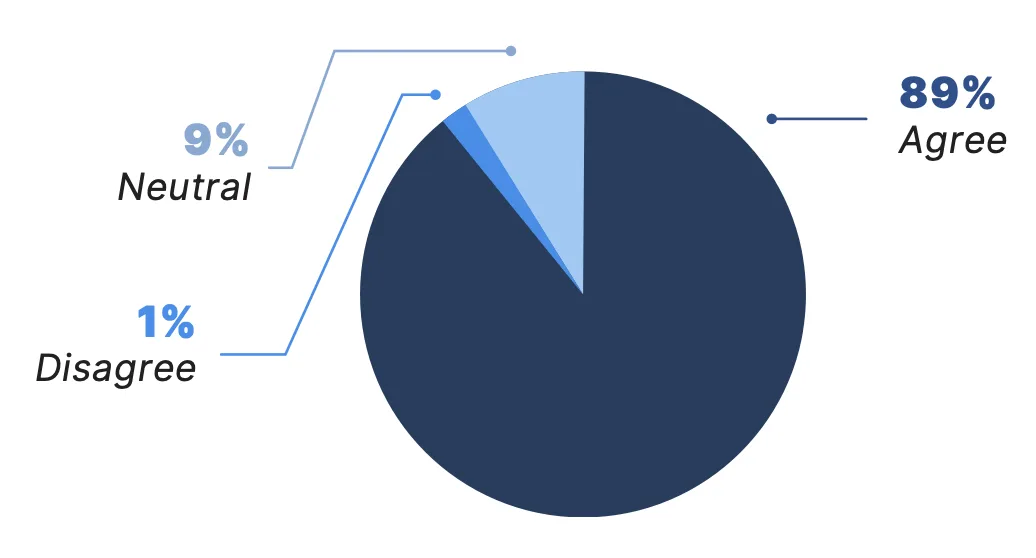
*Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Effects on Treatment Adherence
Most Physicians Report Equivalent or Improved Adherence to Treatment Plans
The convenience and accessibility of telemedicine also appear to be having a positive impact on patient adherence to treatment plans.
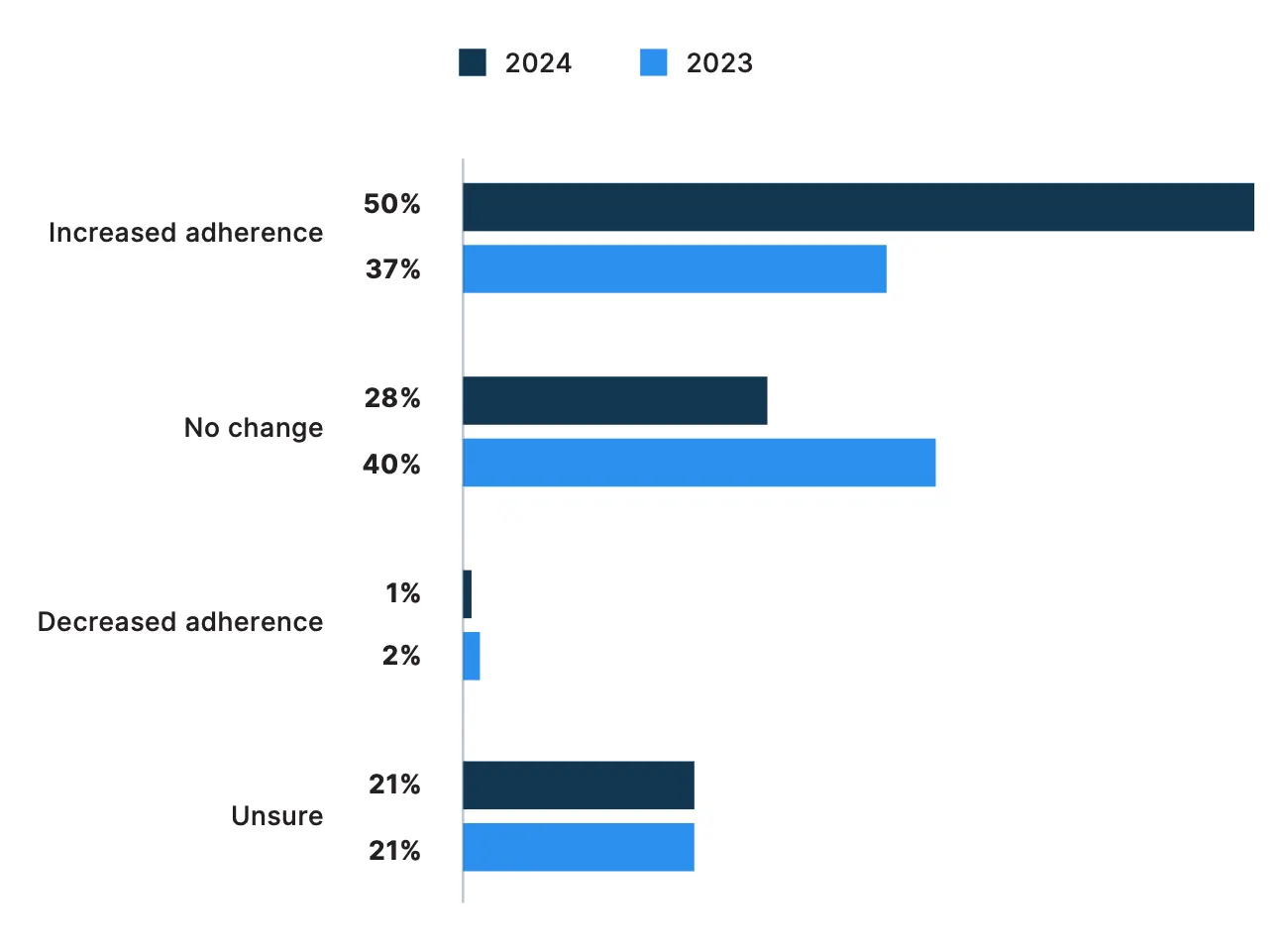
Among physicians surveyed, 78% reported they have observed either equivalent or improved patient adherence to treatment plans through telemedicine. This includes 50% who said telemedicine has led to increased adherence, a substantial increase from 37% last year. In contrast, less than 1% reported decreased adherence.
Survey results also suggest telemedicine could be especially effective at increasing adherence among patients with chronic illnesses. For example, the majority of endocrinologists (56%) and oncologists (55%) surveyed reported increased adherence to treatment plans with telemedicine. Similarly, 55% of primary care physicians — who often play a pivotal role in long-term patient care — also observed better adherence, with none reporting a decrease in adherence.

How has telemedicine affected your patients’ adherence to treatment plans?
Interdependence of Virtual, In-Person Care
Telemedicine Often Best Served as a Complement to In-Person Care
While telemedicine offers a myriad of benefits, it is clear that in-person care remains an essential cornerstone of health care delivery for many physicians and patients. Still, survey results suggest physicians across specialties widely view telemedicine as a powerful complement to in-person care.
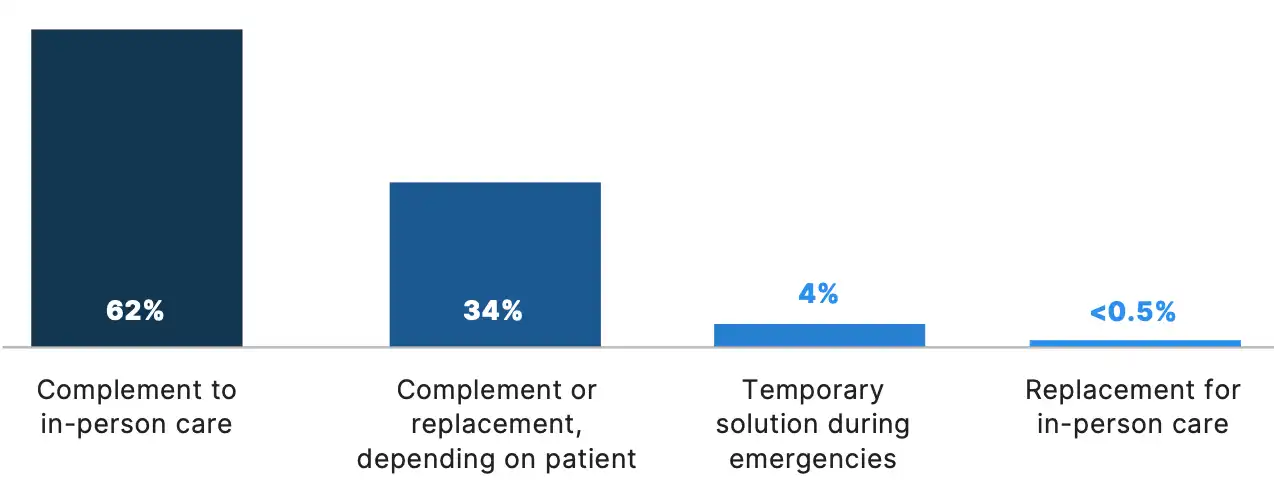
Among physicians surveyed, 96% emphasized telemedicine’s role as a complement to, or on occasion, a replacement to in-person care. Notably, fewer than 0.5% of physicians reported viewing telemedicine as a complete replacement for in-person care. These findings suggest that virtual and in-person care currently work best in tandem, enabling physicians to provide more personalized care to a broader patient population.
Which of the following best describes your perspective on telemedicine?
Permanence of Telemedicine
Physicians Would Like Telemedicine to Have a Permanent Role
The future place of telemedicine appears to be clear for the vast majority of physicians: 83% of those surveyed would like telemedicine to be a permanent part of their clinical practice. Strong physician support for telemedicine underscores its increasing role in modern health care, with the potential to transform how care is delivered for years to come.
Among physicians surveyed, psychiatrists (90%), neurologists (90%), oncologists (88%), and endocrinologists (88%) were some of the most likely to report they want telemedicine to be a permanent part of their practice.
Would you like telemedicine to be a permanent part of your clinical practice?*
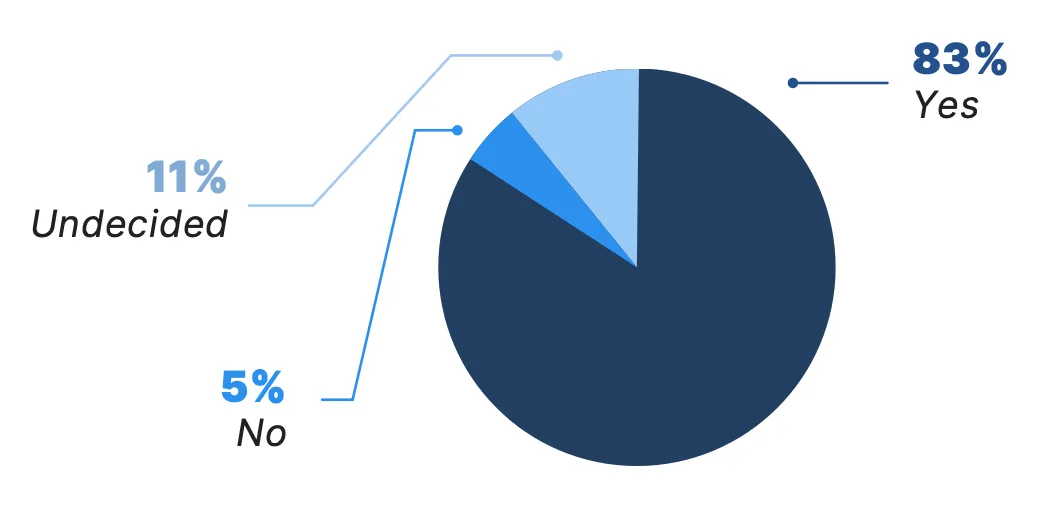
*Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Patient Adoption of Telemedicine
As part of this study, in October 2024, Doximity surveyed 2,400 adult patients across the U.S. about their telemedicine use and preferences for virtual care in the future.
Survey respondents included 1,200 patients who identified as having a chronic illness and 1,200 patients who did not. More than two-thirds of all survey respondents reported they have participated in a telemedicine visit.
The following section details these patients’ direct experiences with telemedicine and explores broader trends in patient use and preferences.
Telemedicine Use Among Patients
Many Patients Continue to Rely on Virtual Care
Among all patients surveyed, 41% reported receiving medical care virtually in the last year (from October 2023 to October 2024).
Survey results indicate that telemedicine is playing a particularly important role in the care of patients with chronic illnesses. Among patients with chronic illnesses, three-fourths (75%) reported they have used virtual care, with 50% doing so in the past year. In comparison, 60% of patients without chronic conditions said they have used telemedicine (32% in the past year). Notably, 61% of patients who had a telemedicine visit in the past year reported having a chronic illness.
Patients with chronic illnesses also reported more frequent use of telemedicine. More than half (55%) of patients with a chronic illness reported using telemedicine three or more times in the past year, compared with 32% of patients without a chronic illness. Notably, more than 18% of patients with a chronic illness received virtual care at least six times over the past year.
Chronic illnesses, which currently affect six in 10 Americans and constitute eight of the 10 leading causes of death in the U.S., are becoming increasingly prevalent, especially in aging populations.4,5,6 These survey findings suggest telemedicine could play a critical role in addressing this public health challenge by ensuring timely and effective access to chronic disease management.
In the past 12 months, about how many times did you meet with a doctor virtually?*†
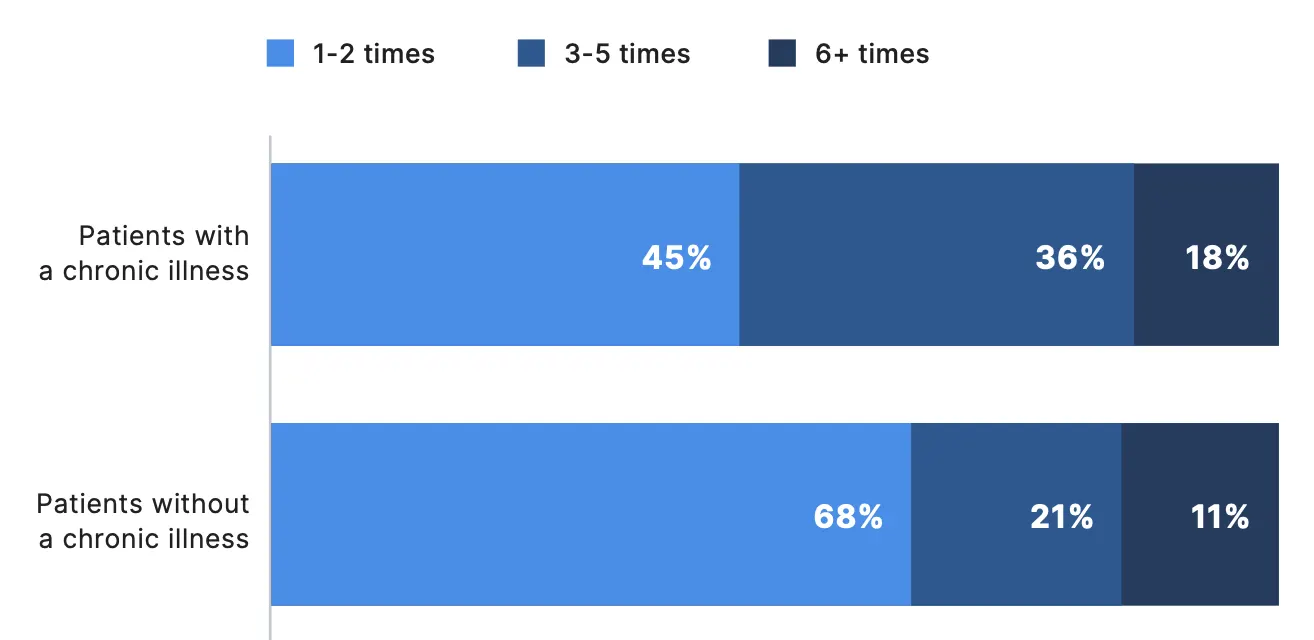
*Percentages reflect respondents who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year
†Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Factors Driving Telemedicine Adoption
Patients Use Telehealth for Convenience, Medication Management
Patients who saw their doctor virtually in the past year cited multiple reasons for using telemedicine, with convenience and ease of use standing out as top factors, according to survey results. Over half (52%) of survey respondents reported one of the reasons they opted for virtual care was because it was easier than an in-person visit, while 48% pointed to its faster access.
For some patients, practical barriers played a key role: 24% said they used virtual care because they faced some sort of difficulty getting to their doctors office in person, such as a personal disability or limited transportation options. Notably, patients with chronic illnesses were two times more likely to cite difficulty getting to their doctor’s office as a key factor for seeking virtual care.
Additionally, 37% of patients reported they turned to telemedicine because they did not think their situation was serious enough for an in-person visit — up from about a quarter of patients last year. These findings underscore telemedicine’s potential as an important triage tool. Indeed, the majority of patients (78%) indicated they would possibly or definitely be more likely to seek care for non-emergency situations if the visit could be virtual. If a virtual visit determines that in-person care is necessary, telemedicine can serve as an effective gateway to direct those patients to the right care setting.
Why did you see your doctor virtually within the past 12 months?*
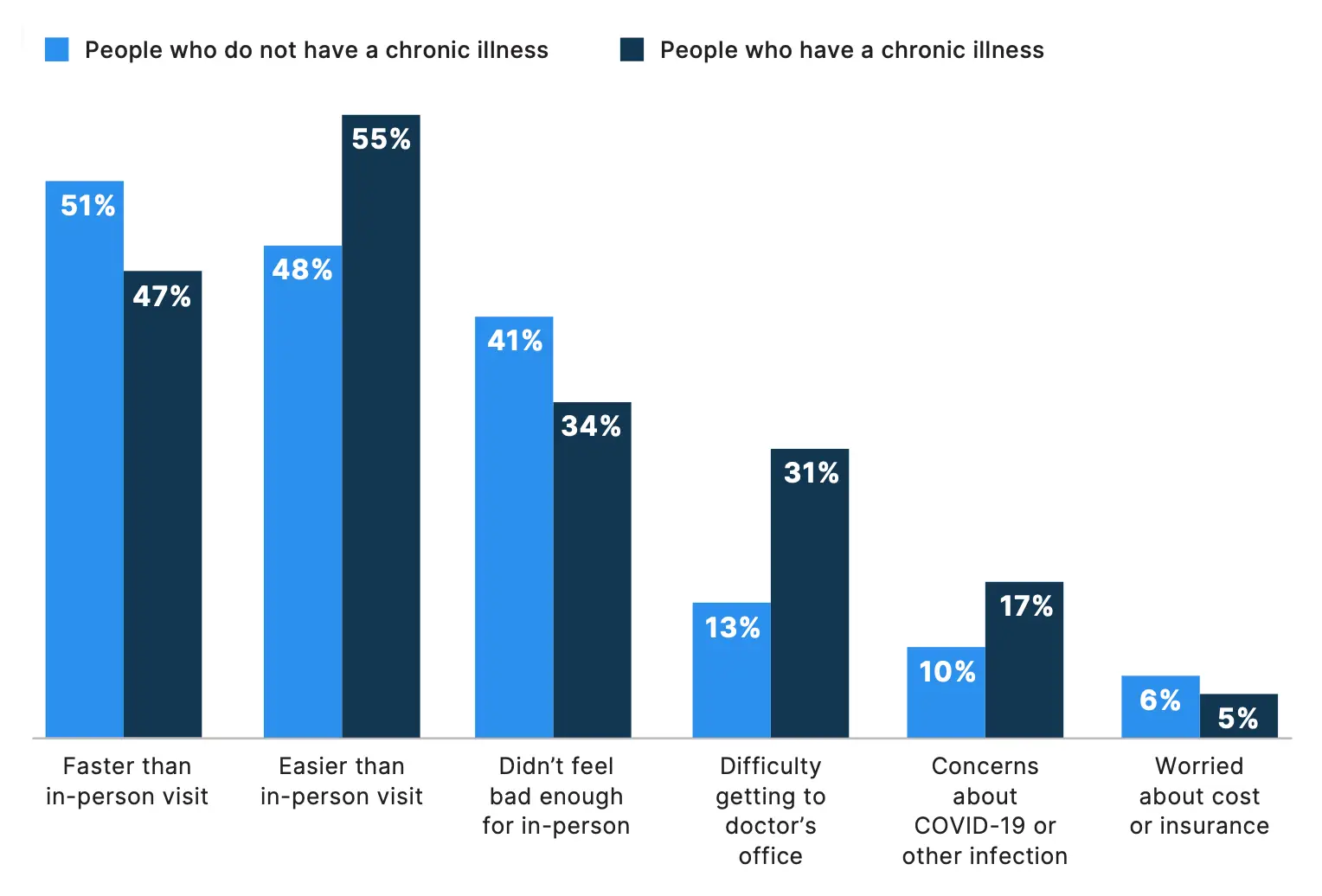
*Percentages reflect respondents who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year
Preferred Uses of Virtual Care
Strong Telemedicine Preference, Adoption for Test Results, Medication Management
There are several scenarios in which patients might prefer telemedicine over an in-person visit. Of note, the majority of all patients surveyed would rather have a virtual visit to review test or lab results (56%); for a follow-up visit after an in-person visit (56%); and for medication management and refills (56%). About a quarter of patients also prefer virtual visits for same-day, non-emergency appointments (27%), mental health appointments (25%), and regular check ups (23%).
Among patients who did receive virtual care in the past 12 months, the most common reasons were for medication management and refills (44%), follow-up visits (43%), and to review test or lab results (42%).

What type(s) of care have you recieved virtually in the past 12 months?*
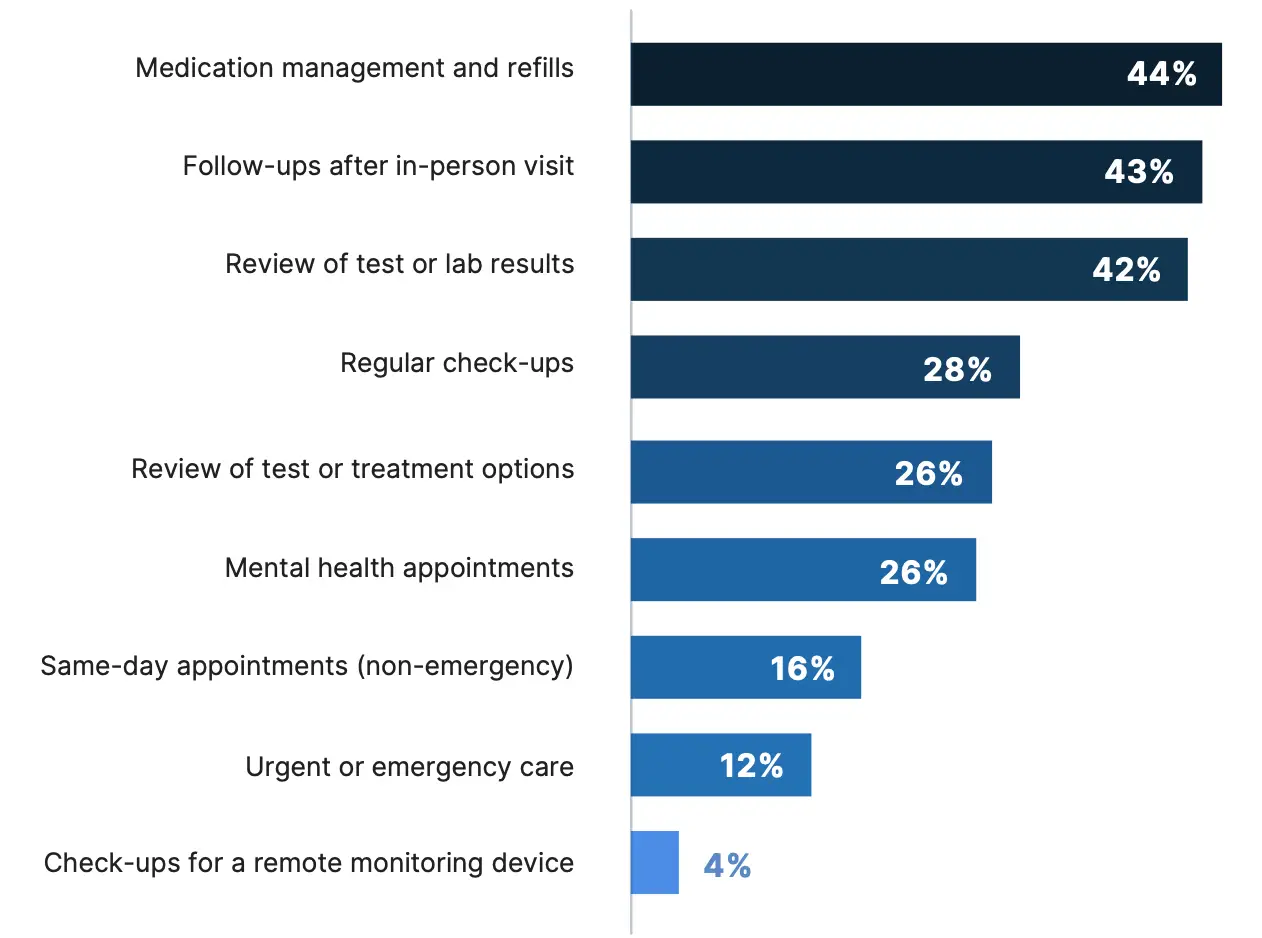
*Percentages reflect respondents who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year
Impact on Overall Health Care, Satisfaction
Patients Report Equivalent or Superior Care, Satisfaction
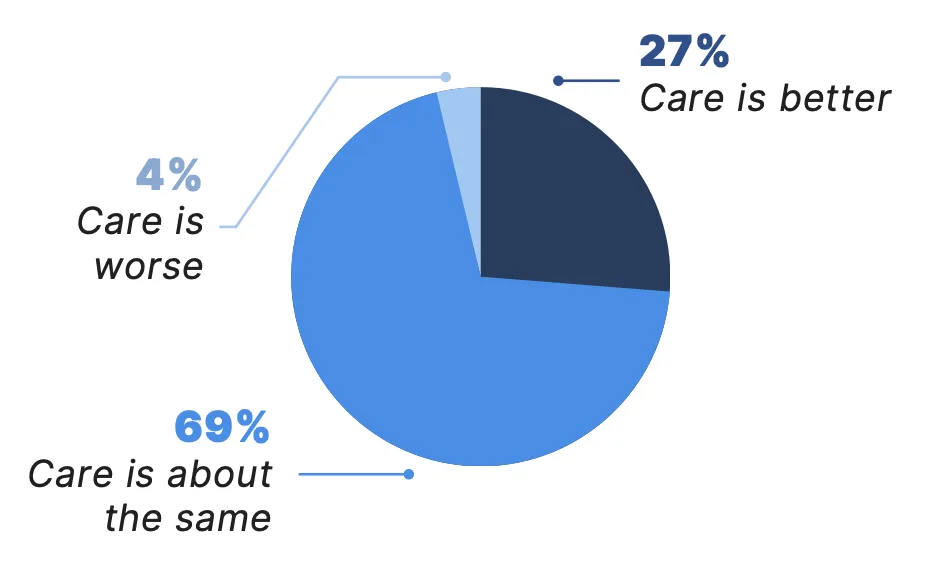
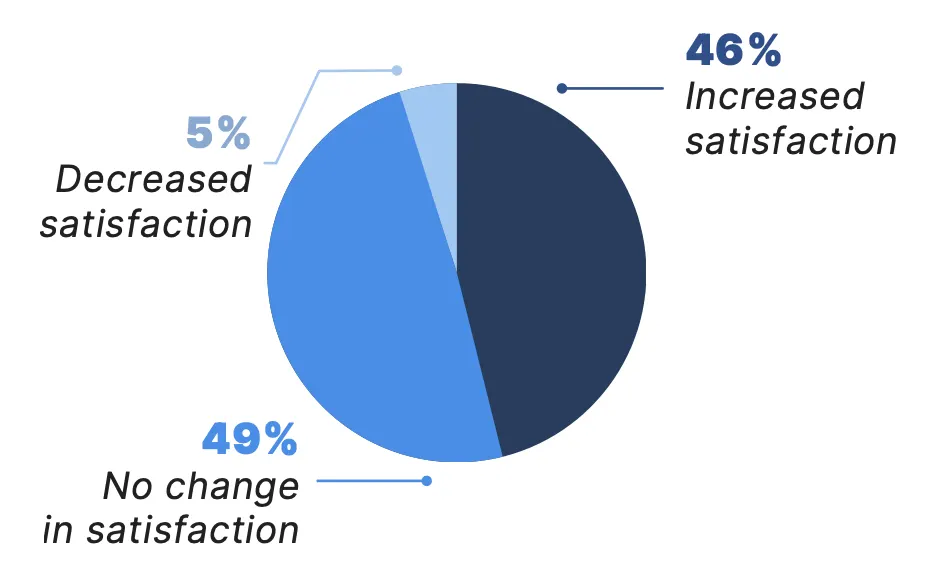
Beyond benefits such as convenience and ease of use, patients with telemedicine experience also reported that it has helped maintain or improve their medical care as a whole. Among patients who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year, the vast majority (96%) said that their overall medical care is about the same or better with virtual care, and 95% reported it has maintained or increased their satisfaction with their care.
Additionally, 82% of these patients reported telemedicine has helped them keep up to date with their health care, rising to 84% for those who have a chronic illness.
Which of the following best represents your experience with virtual care overall?*
How has virtual care affected your satisfaction with your care?*
*Percentages reflect respondents who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year
Impact on Health Care Access, Communication
Patients Report Improved Access, Communication
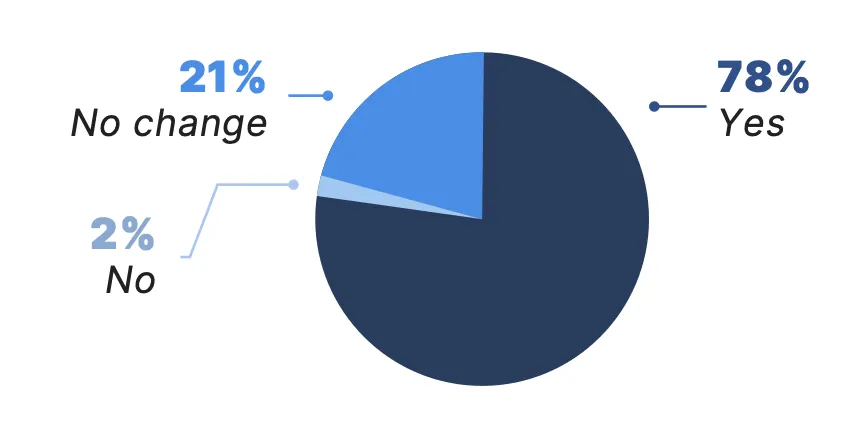
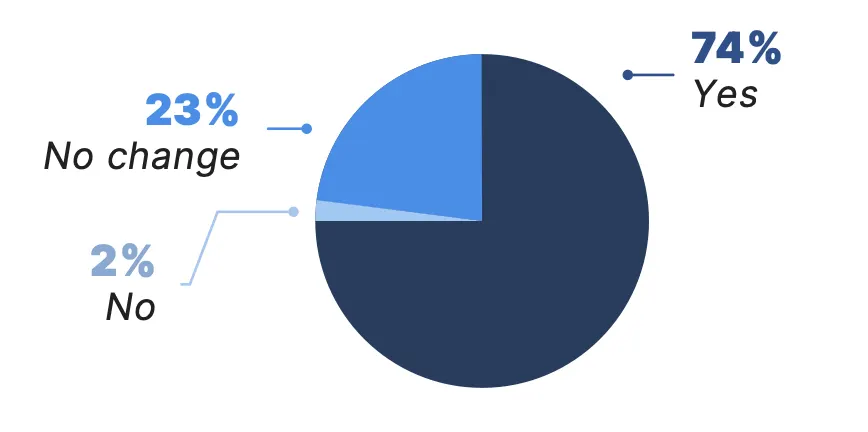
Among patients who received some form of virtual care in the past year, 78% said it has improved their access to health care services, and 74% reported it has improved their communication with their doctors or other health care providers.

Do you believe virtual care has improved your access to health care services?*†
Has virtual care improved communication with your doctors or other health care providers?*†
*Percentages reflect respondents who participated in a telemedicine visit in the past year
†Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Future Expectations for Virtual Care
Patients Appreciate In-Person Care and Favor Continued Access to Telemedicine
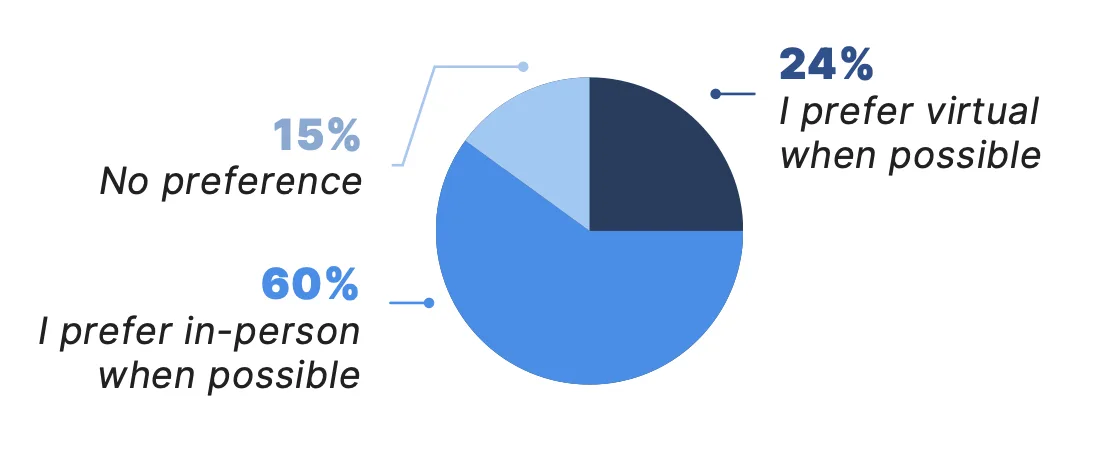
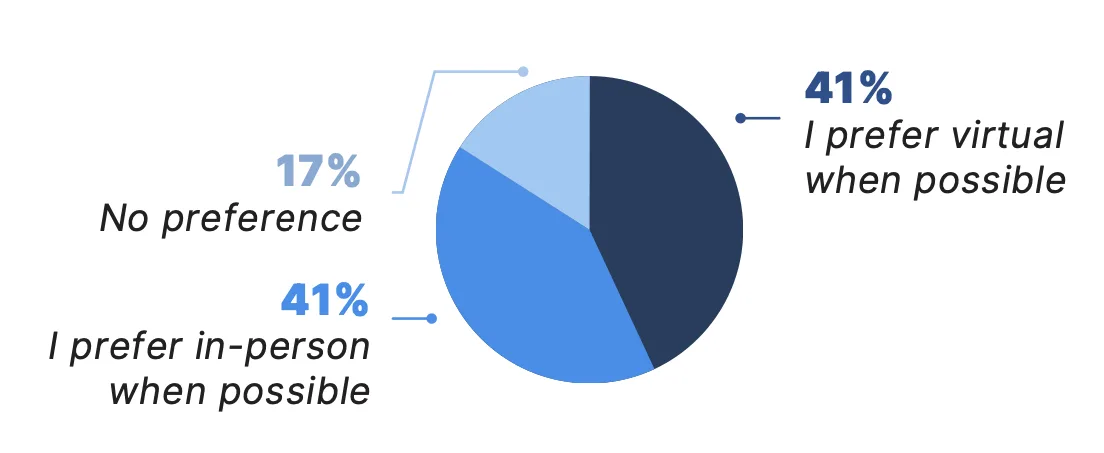
Survey results suggest that the perceived value of telemedicine and preferences for virtual care in the future increase with exposure and familiarity. Nearly a quarter (24%) of all patients surveyed reported they prefer virtual visits when possible, a figure that increases to 41% among those who used telemedicine in the past year and to 55% among patients who participated in three or more telemedicine visits over the past year.
Additionally, more than three out of four patients surveyed (78%) — regardless of prior telemedicine experience — indicated they would like access to virtual care options in the future. This interest increases significantly among those with recent telemedicine experience: 95% of patients who had a telemedicine visit in the past year expressed a desire to retain access to virtual care.
Which of the following best describes how you feel about receiving care virtually compared with in-person?*
All Patients Surveyed
Patients with a Telemedicine Visit Within the Last 12 Months
*Due to rounding, numbers may not sum to 100%.
Lessons from Dialer for Free Clinics
Doximity’s Dialer for Free Clinics program provides unlimited complimentary access to the company’s telehealth platform to free and charitable clinics across the U.S. As of December 2024, Dialer for Free Clinics has supported over 130 free and charitable clinics across the U.S.
The following case studies explore how three Dialer for Free Clinics recipients are using telemedicine to expand access to care in their local communities.
Health Unit on Davison Avenue (HUDA Clinic)
About HUDA Clinic
The Health Unit on Davison Avenue (HUDA Clinic), located in Detroit, cares for patients throughout Northeast Michigan. With only one full-time staff member, HUDA Clinic depends on over 600 volunteers, often with full-time jobs of their own, to care for a growing and aging patient population.
Over the last 24 months, the demand for new patient services at HUDA Clinic has increased by an average of 25% each month. Open just three days a week, the HUDA clinic provided over 10,000 patient visits last year, with telemedicine helping to expand patient access to care while easing demands on volunteers.

Telemedicine Enhances Psychiatric Care and Provider Safety
Almost all of the clinic’s psychiatric appointments are now conducted via telemedicine. This shift not only offers greater flexibility for patients and clinicians, it also allows providers to gain a deeper understanding of their patients’ living conditions. This has proven especially valuable for psychiatric care, where a patient’s environment can have a significant impact on their mental health.
For clinicians in psychiatry, telemedicine has also helped reduce concerns about in-person safety risks, by allowing providers to conduct sessions, which may include very sensitive and triggering topics, remotely.
Telemedicine Enables Volunteers to Reconnect with Their Purpose
For many of the clinic’s volunteers, working at HUDA Clinic is a way to reconnect with the core values and aspirations that drew them to medicine. Wilson explains, “One of our physicians, who recently had a baby, speaks Bangla. We have a huge Bangla-speaking population, and through telemedicine, she can see four patients in an hour and never leave her dining room table.”
Sustaining Quality of Care and Growth Through Telemedicine
In the face of rising demand, HUDA Clinic has embraced telemedicine as a vital tool in delivering accessible, high-quality care to its growing patient base. The flexibility telemedicine offers has proven invaluable, allowing clinicians to balance their volunteer commitments with their personal lives while still contributing meaningfully to patient care. As the clinic continues to adapt to the community’s needs, telemedicine remains at the heart of HUDA Clinic’s strategy.
Volunteer Healthcare Clinic
About Volunteer Healthcare Clinic
Volunteer Healthcare Clinic, located in Austin, Texas, is supported by a small staff and a community of volunteers who donate their time and skills to provide essential care to uninsured adults. Since the pandemic, telemedicine has become a strategic resource, particularly for patients who struggle with transportation challenges and inflexible work schedules that can limit access to health care services. Telemedicine supplements their in-person services by supporting case management, addressing patient questions, and facilitating medication management, ensuring patients receive timely care when an in-person visit is not immediately possible.
Telemedicine’s Ease of Use Helps Volunteers and Staff Provide Consistent Care
Clinic staff and volunteers have quickly adopted and embraced telemedicine for its ease of use. With several volunteers working in rotation, including many who might only work one day a month, ease of use is very important. Case management nurses also rely on telemedicine to handle follow-up calls from home, making sure that care results are communicated and next steps are clearly outlined for patients.
Provides Multiple Touchpoints for Patients Outside the Clinic
Telemedicine at Volunteer Healthcare Clinic has also proven effective for handling various routine needs, such as refilling prescriptions, following up on missed appointments, and reviewing lab results. By offering multiple touchpoints throughout a patient’s care journey, telemedicine allows patients to stay connected with their case workers and medical staff.

Hypertension Control Project Uses Telemedicine for Chronic Disease Management
Volunteer Healthcare Clinic also incorporates telemedicine into its Hypertension Control Project. As part of this project, health guides monitor and regularly check in with patients diagnosed with high blood pressure. With the addition of telemedicine, the health guides can help patients remotely monitor their progress, review blood pressure readings, and stay consistent with their medical appointments. These more frequent, personal touchpoints offer essential support, making sure patients stay engaged with their care and reducing the risk of complications.
Telemedicine is an Integral Part of the Clinic’s Care Model
Telemedicine has become an integral part of Volunteer Healthcare Clinic. By focusing its telemedicine strategy on continuity of care, the clinic has found a sustainable, efficient way to blend virtual care into its overall care delivery model.
Urban Ministries of Wake County Open Door Clinic
About Open Door Clinic
Open Door Clinic provides medical care to uninsured adults in Raleigh, North Carolina. The clinic shifted to telemedicine during the pandemic and has since transitioned to a hybrid model. For many of their patients, this has become a vital service, especially for those facing transportation challenges and financial limitations.
Texting Enhances Continuity of Care and Medication Adherence
A key tool in this shift to telemedicine has been text messaging. Open Door Clinic sends medication guides and photos of over-the-counter products directly to patients’ phones, helping them better manage their treatments. This service has been particularly useful for patients with literacy challenges.
“We can text them materials, handouts, and photos, so they can just take their phone to the drugstore and show the pharmacist what they need,” said Diana Castillo, clinic director.
Open Door Clinic has also found that texting enhances continuity of care, particularly for patients managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
Telemedicine and Text Messaging Support Sustainable Care for the Community
Through telemedicine, the clinic has been able to better support patients and enable their health care providers to operate more efficiently. These continued communications enable busy providers to handle routine follow-ups and lab results remotely, freeing up in-person appointments for more complex cases.
The flexibility of virtual care services ensures the clinic can meet a higher demand of patients while also maintaining a high quality of care.
As the demand for health care services continues to grow, Open Door Clinic is committed to using telemedicine to better serve their community. With telemedicine, they aim to increase patient engagement and ensure that everyone, regardless of their circumstances, has access to the care they need.

Conclusion
Telemedicine has evolved into a valuable complement to in-person care, capable of improving treatment adherence and enhancing patient outcomes. Both patients and physicians recognize the benefits of telemedicine, and the majority would like it to remain part of their health care experience in the future.
Findings from this study suggest that virtual and in-person care are not at odds with one another. Rather, when both modalities are used together, they can strengthen health care delivery and personalize patient care. Telemedicine serves as an essential extension of in-person care, broadening access, enhancing continuity, and deepening the connection between physicians and their patients.
As the U.S. confronts an aging and growing patient population and an intensifying physician shortage, telemedicine will continue to serve as an important tool for addressing gaps in the system and delivering effective, timely care.
Methodology & Sources
Methodology
Physician Insights
Adoption by Age
Responses were drawn from physicians who used Doximity’s telemedicine platform in 2023.
Specialty Rank
The specialty rank list was drawn from physicians who used the Doximity telemedicine platform in 2023. Pediatric specialties and some adult subspecialties were folded into their adult general specialty. For example, pediatric cardiology was included in cardiology.
Physician Survey
Doximity conducted a survey of its physician telemedicine users in August 2024 via SurveyMonkey to supplement its existing physician adoption insights.
This survey was completed by 1,171 U.S. physicians across ten different specialties: cardiology, dermatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, neurology, oncology, primary care, psychiatry, pulmonology, and rheumatology. An additional 131 of Doximity’s nurse practitioner telemedicine users also completed the survey.
Survey participant demographics are not population-based and findings therefore may not be able to be extrapolated to the broader physician population.
Patient Insights
Doximity powered the patient insights section through a survey conducted via Pollfish. This survey included 2,400 U.S. adults. The survey was distributed to two groups: 1,200 respondents who identified as having a chronic illness and 1,200 respondents who identified as not having a chronic illness. Doximity conducted the survey in October 2024. Survey participant demographics are not population-based and findings therefore may not be able to be extrapolated to the general population.

References
- 1The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2021 to 2036. Association of American Medical Colleges.
- 2Recent Changes in Physician Practice Arrangements: Shifts Away from Private Practice and Towards Larger Practice Size Continue Through 2022. American Medical Association.
- 3Stefos T; Carey K; Shen M-L; Poe S; Oh DH; Moran E. The Effect of Telehealth Services on Provider Productivity. Medical Care. 2021 May;59(5):456-460.
- 4Chronic Diseases in America. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- 5Leading Causes of Death. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- 6Ansah JP and Chiu C-T. Projecting the Chronic Disease Burden Among the Adult Population in the United States Using a Multi-State Population Model. Frontiers in Public Health. 2023 January;10:1082183.